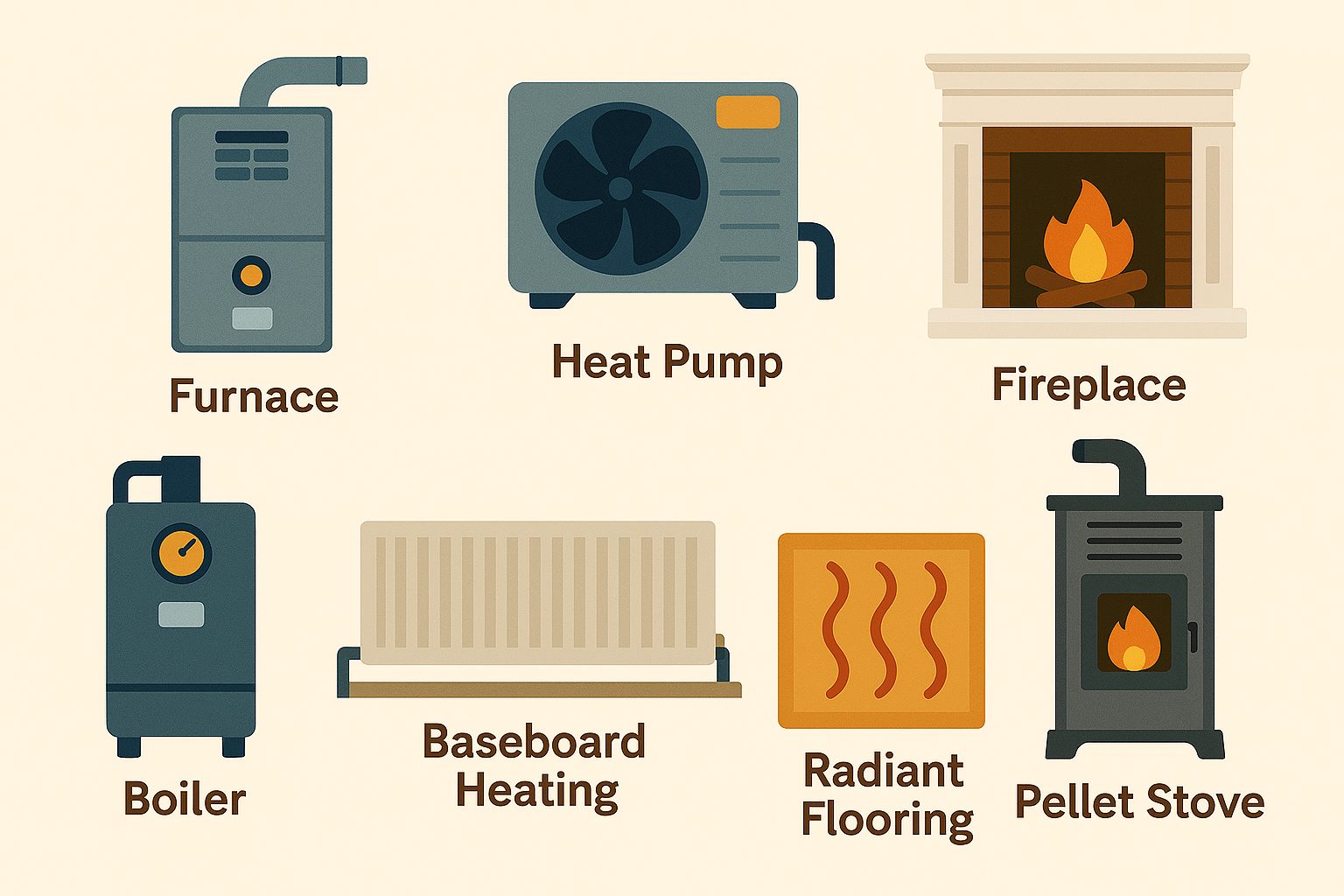
🔥 Understanding the Different Types of Home Heating Systems
As the crisp air of fall settles in, homeowners begin to think about staying warm through the colder months. Whether you’re buying a new home, upgrading your current system, or just curious about your options, understanding the different types of heating systems can help you make informed decisions. Let’s break down the most common types:
🏠 1. Furnaces (Forced Air Systems)
How it works: Heats air and distributes it through ducts using a blower. Fuel options: Natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity. Pros:
- Fast heating
- Can be combined with central AC
- Widely available Cons:
- Can be noisy
- Requires ductwork
🌡️ 2. Boilers (Radiant Heat Systems)
How it works: Heats water and sends it through radiators or underfloor pipes. Fuel options: Natural gas, oil, or electricity. Pros:
- Quiet operation
- Even, comfortable heat
- No ductwork needed Cons:
- Slower to heat up
- More expensive to install
🔌 3. Heat Pumps
How it works: Transfers heat from outside air or ground into the home. Types: Air-source and ground-source (geothermal). Pros:
- Energy efficient
- Provides both heating and cooling
- Lower operating costs Cons:
- Less effective in very cold climates (air-source)
- Higher upfront cost (geothermal)
🔥 4. Fireplaces
How it works: Burns wood, gas, or electricity to produce radiant heat. Types: Traditional wood-burning, gas, and electric fireplaces. Pros:
- Adds ambiance and charm
- Can serve as a backup heat source
- Ideal for zone heating Cons:
- Limited heat output
- Requires ventilation (wood/gas)
- Regular maintenance and cleaning
🔌 5. Electric Baseboard Heaters
How it works: Uses electric resistance to heat individual rooms. Pros:
- Easy to install
- Good for zone heating
- No ductwork required Cons:
- Higher electricity costs
- Limited temperature control
🪵 6. Wood and Pellet Stoves
How it works: Burns wood or pellets to produce heat. Pros:
- Cozy ambiance
- Renewable fuel source
- Great for off-grid homes Cons:
- Requires manual fueling
- Needs ventilation and regular cleaning
🌬️ 7. Radiant Floor Heating
How it works: Warm water or electric coils run beneath the floor. Pros:
- Luxurious comfort
- Silent operation
- Energy efficient Cons:
- High installation cost
- Slow to adjust temperature
🧊 Bonus: Hybrid Systems
Combines a furnace with a heat pump to optimize efficiency based on outdoor temperatures.
🛠️ Final Thoughts
Choosing the right heating system depends on your climate, budget, home layout, and energy goals. As fall approaches, it’s a great time to assess your current setup and consider upgrades that could improve comfort and efficiency.
Would you like me to add a call-to-action or SEO keywords to help this blog post rank better? I can also tailor it to your local market or audience.

 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link